Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C
CNguyen, B. V. C.*; 村上 健太*; Chena, L.*; Phongsakorn, P. T.*; Chen, X.*; 橋本 貴司; Hwang, T.*; 古澤 彰憲; 鈴木 達也*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 39, p.101639_1 - 101639_9, 2024/06
In reactor pressure vessel materials, the formation of Mn- and Ni-rich nanoclusters is a major cause of neutron irradiation embrittlement. The segregation of these solute atoms into dislocation loops has attracted attention as a mechanism to accelerate solute clustering. In this study, the behaviors of solute Mn and Ni atoms in Fe-0.6wt.%Ni, Fe-1.4wt.%Mn, and Fe-1.4wt.%Mn-0.6wt.%Ni alloys irradiated at 400  C up to 3 dpa were analyzed using three-dimensional atom probe tomography. Solute atom clusters were observed in all materials, and their shapes were spherical, flat, and torus in FeNi, FeMn, and FeMnNi, respectively. In ternary alloy FeMnNi, Mn and Ni atoms were concentrated in the sample in the form of arcs, and the orientation of the plane containing the arcs was estimated by comparing field desorption images. The size, number density, and orientation of this structure were found to be in good agreement with those of both types of dislocation loops, namely, b = 1/2
C up to 3 dpa were analyzed using three-dimensional atom probe tomography. Solute atom clusters were observed in all materials, and their shapes were spherical, flat, and torus in FeNi, FeMn, and FeMnNi, respectively. In ternary alloy FeMnNi, Mn and Ni atoms were concentrated in the sample in the form of arcs, and the orientation of the plane containing the arcs was estimated by comparing field desorption images. The size, number density, and orientation of this structure were found to be in good agreement with those of both types of dislocation loops, namely, b = 1/2  111
111 and b =
and b =  100
100 , identified in a previous study using the same material. The positions of Ni and Mn enrichment did not fully overlap. Ni atoms tended to be concentrated more in the inner part of the loop than the Mn atoms. Mn atoms were enriched only in the vicinity of the dislocation loops, whereas Ni atoms showed a higher concentration inside the dislocation loops than in the bulk.
, identified in a previous study using the same material. The positions of Ni and Mn enrichment did not fully overlap. Ni atoms tended to be concentrated more in the inner part of the loop than the Mn atoms. Mn atoms were enriched only in the vicinity of the dislocation loops, whereas Ni atoms showed a higher concentration inside the dislocation loops than in the bulk.
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; Li, Y.; 眞崎 浩一*; 高越 大輝*; 永井 政貴*; 南日 卓*; 村上 健太*; 関東 康祐*; 八代醍 健志*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00484_1 - 22-00484_13, 2023/08
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code, PASCAL, has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency for failure probability and failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. To strengthen the applicability of PASCAL, considerable efforts on verifications of the PASCAL code have been made in the past years. As a part of the verification activities, a working group consisted of different organizations from industry, universities and institutes, was established in Japan. In the early phase, the working group focused on verifying the PFM analysis functions for RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) subjected to pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. Recently, the PASCAL code has been improved in order to run PFM analyses for both RPVs in PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients. Simultaneously, the working group initiated a verification plan for the improved PASCAL through independent PFM analyses by different organizations. Concretely, verification analyses for a PWR-type RPV subjected to PTS transients and a BWR-type RPV subjected to a low-temperature over pressure transient were performed using PASCAL. This paper summarizes those verification activities, including the verification plan, analysis conditions and results. Based on the verification studies, the reliability of PASCAL for probabilistic integrity assessments of Japanese RPVs was confirmed with confidence.
安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(5), p.1742 - 1756, 2023/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is a significant issue when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. After the Fukushima-Daiichi accident in Japan, we have investigated in-depth the hydrogen transport mechanisms by utilizing experimental and numerical approaches. Computational fluid dynamics is a powerful tool for better understanding the transport behavior of gas mixtures, including hydrogen. This paper describes a large-eddy simulation of gas mixing driven by a high-buoyancy flow. We focused on the interaction behavior of heat and mass transfers driven by the horizontal high-buoyant flow during density stratification. For validation, the experimental data of the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility were used. With a high-power heater for the gas-injection line in the CIGMA facility, a high temperature flow of approximately 390 C was injected into the test vessel. By using the CIGMA facility, we can extend the experimental data to the high temperature region. The phenomenological discussion in this paper help understand the heat and mass transfer induced by the high-buoyancy flow in the containment vessel during a severe accident.
C was injected into the test vessel. By using the CIGMA facility, we can extend the experimental data to the high temperature region. The phenomenological discussion in this paper help understand the heat and mass transfer induced by the high-buoyancy flow in the containment vessel during a severe accident.
佐藤 拓未; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; Quaini, A.*; Gu neau, C.*
neau, C.*
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 79, p.102481_1 - 102481_11, 2022/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Thermodynamics)Investigation of the primary containment vessel inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station showed that a significant amount of the molten corium reached the bottom of the pedestal region. The molten corium and concrete likely caused a complex interaction called Molten Corium Concrete Interaction. The solidification hysteresis of these ex-vessel debris significantly influences its properties. We performed a thermodynamic analysis using the TAF-ID database to infer the solidification path of U-Zr-Al-Ca-Si-O molten corium, which was chosen for a prototypic system of ex-vessel debris. The solidification path for the CaO-rich sim-corium showed that (i) melting as a single liquid phase above 2430 K, (ii) selective solidification of the oxide-rich corium mainly consisted of fuel materials, and (iii) solidification of the remaining materials as a silicate matrix. In contrast, the solidification path for the SiO -rich corium indicated that (i) formation of liquid miscibility gap above 2200 K between U-rich and Zr-rich oxidic melts, (ii) individual precipitation of solid phases in each liquid phase.
-rich corium indicated that (i) formation of liquid miscibility gap above 2200 K between U-rich and Zr-rich oxidic melts, (ii) individual precipitation of solid phases in each liquid phase.
Hamdani, A.; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104415_1 - 104415_16, 2022/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:66.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis and validation works from the previous experimental study on the natural convection driven by outer surface cooling in the presence of density stratification consisting of air and helium (as a mimic gas of hydrogen). The experiment was conducted in the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The numerical simulation was carried out to analyze the detailed effect of the cooling region on the erosion of the helium stratification layer. The temporal and spatial evolution of the helium concentration and the gas temperature inside the containment vessel was predicted and validated against the experimental data. In addition, two stratification behaviors that depend on the cooling location were presented and discussed. The CFD simulation confirmed that an upper head cooling caused two counter-rotating vortexes in the helium-rich zone. Meanwhile, the upper half body cooling caused two counter-rotating vortexes in the helium-poor zone. These findings are important to understand the mechanism of the density stratification process driven by natural convection in the containment vessel.
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 199, p.104706_1 - 104706_13, 2022/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:58.29(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL was developed in Japan for probabilistic integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) transients. To strengthen the practical applications of PFM methodology in Japan, PASCAL has been upgraded to a new version, PASCAL5, which enables PFM analyses of RPVs in both PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients, including PTS and normal operational transients. In this paper, the recent improvements in PASCAL5 are described such as the incorporated stress intensity factor solutions and corresponding calculation methods for external surface cracks and embedded cracks near the RPV outer surface. In addition, the analysis conditions and evaluation models recommended for PFM analyses of Japanese RPVs in BWRs are investigated. Finally, PFM analysis examples for core region of a Japanese BWR-type model RPV subjected to two transients (i.e., low-temperature over pressure and heat-up transients) are presented using PASCAL5.
小野田 雄一; 山野 秀将
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/10
原子力機構におけるナトリウム冷却高速炉の設計では、シビアアクシデントが生じた場合に、さまざまな設計対策により損傷炉心物質を原子炉容器内で安定的に冷却する方針(炉容器内保持: IVR)をとっている。IVRに失敗する可能性は非常に低いものの、確率論的リスク評価の研究では、IVRの失敗を含むさまざまなシナリオの検討が必要となる。そこで本研究では、原子炉容器内におけるデブリの安定冷却に関わる事象スペクトルを幅広く検討するため、コアキャッチャーのスカート部にデブリが堆積する場合の原子炉容器の変形・破損挙動を、構造解析コードFNAS-STARを用いて数値的に解析した。原子炉容器の破損条件を調査する観点から、出力密度の異なる2ケースの解析を実施した。今回の想定条件下における高出力密度のケースでは、原子炉容器の温度が約1100 Cに達すると原子炉容器が大幅に変形し、その破損判断基準に到達した。
Cに達すると原子炉容器が大幅に変形し、その破損判断基準に到達した。
石垣 将宏*; 安部 諭; Hamdani, A.; 廣瀬 意育
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 168, p.108867_1 - 108867_20, 2022/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:76.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to improve computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis accuracy to estimate thermal flow in a containment vessel during a severe accident. Previous studies pointed out the importance of the influence of initial and boundary conditions on the CFD analysis. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the influence of initial and boundary conditions by numerical analysis of natural convection experiments in a large containment vessel test facility CIGMA(Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus). A density stratification layer was initially formed in the vessel using helium and air, and external cooling of the vessel surface-induced natural convection. In this study, we carried out numerical simulations of the density stratification erosion driven by the natural convection using the RANS (Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes) model. As a result, the temperature boundary condition of the small internal structure in the vessel had a significant influence on the fluid temperature distribution in the vessel. The erosion velocity of the density stratification layer changed depending on the initial gas concentration distribution. Then, appropriate settings of the temperature and gas concentration conditions are necessary for accurate analysis.
佐藤 一憲; 山路 哲史*; Li, X.*; 間所 寛
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 9(2), p.21-00436_1 - 21-00436_17, 2022/04
Interpretation for the two-week long Unit 3 ex-vessel debris cooling behavior was conducted based on the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) data and the site data such as pressure, temperature, gamma ray level and live camera pictures. It was estimated that the debris relocated to the pedestal was in partial contact with liquid water for about initial two days. With the reduction of the sea water injection flowrate, the debris, existed mainly in the pedestal region, became "dry", in which the debris was only weakly cooled by vapor and this condition lasted for about four days until the increase of the sea water injection. During this dry period, the pedestal debris was heated up and it took further days to re-flood the heated up debris.
神山 健司; 松場 賢一; 加藤 慎也; 今泉 悠也; Mukhamedov, N.*; Akayev, A.*; Pakhnits, A.*; Vurim, A.*; Baklanov, V.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/04
To achieve in-vessel retention for mitigating the consequences of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors, controlled material relocation (CMR) has been proposed as an effective safety concept. CMR is not only aiming at eliminating the potential for exceeding prompt criticality events that affect the integrity of the reactor vessel, but also enhancing the potential for the in-vessel cooling of degraded core materials during CDAs. Based on this concept several design measures have been studied, and, to evaluate their effectiveness, experimental evidences to show relocation of molten-core material were required. With this background, a series of experimental program called EAGLE (Experimental Acquisition of Generalized Logic to Eliminate re-criticalities) has been carried out collaboratively over 20 years between Japan Atomic Energy Agency and National Nuclear Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan (NNC/RK) using an out-of-pile and in-pile test facilities of NNC/RK. The EAGLE program is divided into three phases, they are called EAGLE-1, EAGLE-2 and EAGLE-3, to cover whole phase after core-melting begins. The subject for EAGLE-1 and the first half of EAGLE-2 is CMR in the early phase of CDA in which the core melting progresses rapidly driven by positive reactivity insertions. The subject for the latter half of EAGLE-2 and whole EAGLE-3 is CMR in the later phase of CDA in which the gradual core melting by decay heat and relocation and cooling of degraded core materials occurs. In the paper, the major achievement of the EAGLE program and future plans are presented.
安部 諭; Hamdani, A.; 石垣 将宏*; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 166, p.108791_1 - 108791_18, 2022/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:64.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes an experimental investigation of natural convection driven by outer surface cooling in the presence of density stratification consisting of an air-helium gas mixture (as mimic gas of hydrogen) in an enclosed vessel. The unique cooling system of the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (whose test vessel is a cylinder with 2.5-m diameter and 11-m height) is used, and findings reveal that the cooling location relative to the stratification plays an important role in determining the interaction behavior of the heat and mass transfer in the enclosed vessel. When the cooling region is narrower than the stratification thickness, the density-stratified region expands to the lower part while decreasing in concentration (stratification dissolution). When the cooling region is wider than the stratification thickness, the stratification is gradually eroded from the bottom with decreasing layer thickness (stratification breakup). This knowledge is useful for understanding the interaction behavior of heat and mass transfer during severe accidents in nuclear power plants.
松本 俊慶; 岩澤 譲; 杉山 智之
Proceedings of Reactor core and Containment Cooling Systems, Long-term management and reliability (RCCS 2021) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/10
本研究ではBWRのシビアアクシデント(SA)時のウェットキャビティ戦略(事前注水方策)の下での格納容器内デブリ冷却性を評価するための方法論的枠組みを開発している。この評価手法を実証するために、戦略下での格納容器内デブリの冷却成功確率を解析した。炉心溶融進展に関連する5つのパラメータの不確実さを考慮したMELCORコードによる多ケース解析によりRPVから放出される溶融物条件の確率分布を取得した。パラメータセットは、ラテン超方格サンプリング(LHS)によって生成した。JASMINEコードにより水中及び床面上の溶融物の挙動を予測し、アグロメレーション(凝集)及びメルトプールの質量を予測した。JASMINEコード解析のための59個の入力パラメータセットは、MELCOR解析の結果から決定した溶融物条件の確率分布を用いて、再度LHSにより生成した。複数のキャビティ内初期水プール深さ条件でJASMINE解析を行い、堆積デブリ高さをMCCI発生の判定基準値と比較した。判定結果を集計することで溶融物の冷却成功確率を求めた。
Li, C.-Y.; 内堀 昭寛; 高田 孝; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; 岡本 孝司*
第25回動力・エネルギー技術シンポジウム講演論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2021/07
溶融炉心の原子炉容器内保持を達成するためには、デブリベッドの安定冷却と再臨界回避が重要である。本研究では、異なる物質から構成され、密度成層化したデブリベッドの挙動を評価するため、数値流体力学(CFD),個別要素法(DEM),モンテカルロ法を連成させた解析手法を構築した。本解析手法により、デブリベッドにおける密度成層化の挙動等を解析できることを確認した。
岩田 景子; 端 邦樹; 飛田 徹; 廣田 貴俊*; 高見澤 悠; 知見 康弘; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
The crack arrest fracture toughness, K , values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T
, values for highly-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels are estimated according to a linear relationship between crack arrest toughness reference temperature, T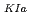 , and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T
, and the temperature corresponding to a fixed arrest load, equal to 4 kN, T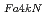 , obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T
, obtained by instrumented Charpy impact test. The relationship between T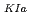 derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T
derived from the instrumented Chrapy impact test and fracture toughness reference temperature, T , was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K
, was expressed as an equation proposed in a previous report. The coefficients in the equation could be fine-tuned to obtain a better fitting curve using the present experimental data and previous K data. The K
data. The K curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3
curve for RPV;A533B class1 steels irradiated up to 1.3 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) was compared with a K
1 MeV) was compared with a K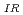 curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K
curve defined in JEAC4206-2016. It was shown that the K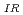 curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K
curve was always lower than the 1%ile curve of K for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K
for these irradiated RPV steels. This result indicates that the conservativeness of the method defined in JEAC4206-2016 to evaluate K using K
using K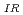 curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
curve is confirmed for highly-irradiated RPV steels.
竹田 武司
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-006, 61 Pages, 2021/04
ROSA-V計画において、大型非定常実験装置(LSTF)を用いた実験(実験番号: SB-PV-09)が2005年11月17日に行われた。ROSA/LSTF SB-PV-09実験では、加圧水型原子炉(PWR)の1.9%圧力容器頂部小破断冷却材喪失事故を模擬した。このとき、非常用炉心冷却系(ECCS)である高圧注入系の全故障と蓄圧注入(ACC)タンクから一次系への非凝縮性ガス(窒素ガス)の流入を仮定した。実験では、上部ヘッドに形成される水位が破断流量に影響を与えることを見出した。アクシデントマネジメント(AM)策として、両ループの蒸気発生器(SG)逃し弁開放によるSG二次側減圧を炉心出口最高温度が623Kに到達した時点で開始した。SG二次側圧力が一次系圧力に低下するまで、このAM策は一次系減圧に対して有効とならなかった。一方、炉心出口温度の応答が遅くかつ緩慢であるため、模擬燃料棒の被覆管表面最高温度がLSTFの炉心保護のために予め決定した値(958K)を超えたとき、炉心出力は自動的に低下した。炉心出力の自動低下後、低温側配管内でのACC水と蒸気の凝縮により両ループのループシールクリアリング(LSC)が誘発された。LSC後、炉心水位が回復して炉心はクエンチした。ACCタンクから窒素ガスの流入開始後、一次系とSG二次側の圧力差が大きくなった。ECCSである低圧注入系の作動を通じた継続的な炉心冷却を確認後、実験を終了した。本報告書は、ROSA/LSTF SB-PV-09実験の手順、条件および実験で観察された主な結果をまとめたものである。
佐藤 一憲; 荒井 雄太*; 吉川 信治
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.434 - 460, 2021/04
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:70.8(Nuclear Science & Technology)The vapor formation within the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is regarded to represent heat removal from core materials to the coolant, while the hydrogen generation within the RPV is regarded to represent heat generation by metal oxidation. Based on this understanding, the history of the vapor/hydrogen generation in the in-vessel phase of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 was evaluated based on the comparison of the observed pressure data and the GOTHIC code analysis results. The resultant vapor/hydrogen generation histories were then converted to heat removal by coolant and heat generation by oxidation. The effects of the decay power and the heat transfer to the structures on the core material energy were also evaluated. The core materials are suggested to be significantly cooled by water within the RPV, especially when the core materials are relocated to the lower plenum.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; 吉村 忍*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(2), p.021505_1 - 021505_8, 2021/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.06(Engineering, Mechanical)Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is considered to be a promising methodology in structural integrity assessments of pressure-boundary components in nuclear power plants since it can rationally represent the inherent probabilistic distributions for influence parameters without over-conservativeness. To strengthen the applicability of PFM methodology in Japan, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL4 which enables the failure frequency evaluation of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and thermal transients. PASCAL4 is expected to make a significant contribution to the probabilistic integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs. In this study, PFM analysis for a Japanese model RPV in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) was conducted using PASCAL4, and the effects of nondestructive examination (NDE) and neutron flux reduction on failure frequencies of the RPV were quantitatively evaluated. From the analysis results, it is concluded that PASCAL4 is useful for probabilistic integrity assessments of embrittled RPVs and can enhance the applicability of PFM methodology.
安部 諭; Studer, E.*; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 368, p.110785_1 - 110785_14, 2020/11
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:78.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is one of the significant issues raised when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool for better understanding the turbulence transport behavior of a gas mixture, including hydrogen. Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) is a practical-use approach for simulating the averaged gaseous behavior in a large and complicated geometry, such as a nuclear containment vessel; however, some improvements are required. We implemented the dynamic modeling for  based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for
on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for  is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
松本 俊慶; 岩澤 譲; 安島 航平*; 杉山 智之
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2020 (ASRAM 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/11
本研究では、事前注水した格納容器内デブリの冷却確率を評価した。まず、落下溶融物条件を求めるため、シビアアクシデント解析コードMELCORによる不確かさ解析を行った。この解析では炉心の溶融・移行過程に関連する5つの不確かさパラメータを選択し、仮定された確率分布を用いて、ラテン超方格法(LHS)により入力パラメータセットを生成した。これを用いたMELCORによる多ケース解析の結果から落下溶融物条件を抽出した。次に、MELCOR解析結果をもとに、パラメータの確率分布を決定し、LHSにより生成した59個のパラメータセットを用いてJASMINEコードによる水中の溶融物挙動の解析を行った。水位の条件は0.5m, 1.0m及び2.0mとした。広がり半径とデブリ質量の解析結果からデブリの堆積高さを求め、判定基準と比較することで冷却の成否判定を行った。以上の一連の解析の結果、デブリ冷却の成功確率を求めた。また、MELCOR及びJASMINEを組み合わせた冷却性解析の課題について論じた。
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(5), p.051501_1 - 051501_10, 2020/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:15.42(Engineering, Mechanical)Structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) is essential for the safe operation of nuclear power plants. For RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs), the assessment should be performed by considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. To assess the structural integrity of an RPV, a traditional method is usually employed by comparing fracture toughness of the RPV material with the stress intensity factor ( ) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,
) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,  of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on
of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on  calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for
calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for  calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.